How many businesses sell only one product? The reality is that firms usually offer a diverse product line, and the individual products will have different selling prices, contribution margins, and contribution margin ratios. Yet, the firm’s total fixed cost picture may be the same, no matter the mix of products sold. This can cloud the ability to perform simple CVP analysis. To lift this cloud requires some knowledge of the product mix.
Assume Hummingbird Feeders produces and sells a brightly colored feeding container for $15 (variable cost of production is $10, and contribution margin is $5) and a nectar formula for $3 per packet ($1 variable cost to produce, resulting in a $2 contribution margin). Hummingbird Feeders sells 10 packets of nectar for every feeder sold. Its fixed cost is $100,000.
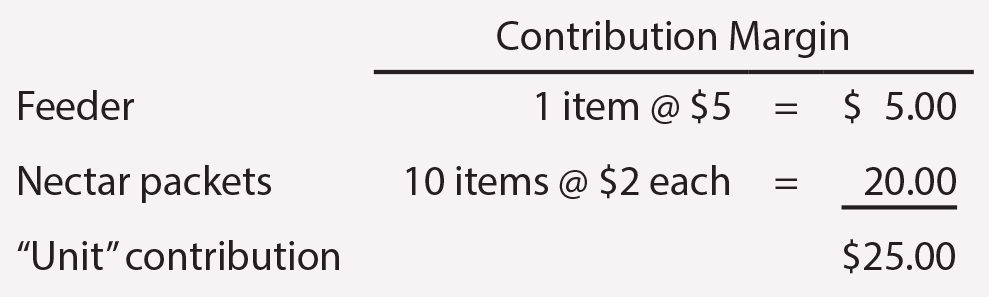 How many feeders and packets must be sold to break even? To answer this question requires a redefinition of the “unit.” Assume the “unit” is 1 feeder and 10 packets. See that each “unit” would have a contribution margin of $25, as shown.
How many feeders and packets must be sold to break even? To answer this question requires a redefinition of the “unit.” Assume the “unit” is 1 feeder and 10 packets. See that each “unit” would have a contribution margin of $25, as shown.
 To recover $100,000 of fixed cost, at $25 of contribution per “unit,” would require selling 4,000 “units” ($100,000/$25). To be clear, this translates into 4,000 feeders and 40,000 packets of nectar. Total break-even sales would be $180,000 (($15 X 4,000 feeders) + ($3 X 40,000 packets)).
To recover $100,000 of fixed cost, at $25 of contribution per “unit,” would require selling 4,000 “units” ($100,000/$25). To be clear, this translates into 4,000 feeders and 40,000 packets of nectar. Total break-even sales would be $180,000 (($15 X 4,000 feeders) + ($3 X 40,000 packets)).
Of course, the validity of this analysis depends upon actual sales occurring in the predicted ratio. Changes in product mix will result in changes in break-even levels.
If Hummingbird Feeders sold $180,000 in feeders, and no packets of nectar, it would come nowhere near break-even (because the contribution margin ratio on feeders is much lower than on the packets of nectar).
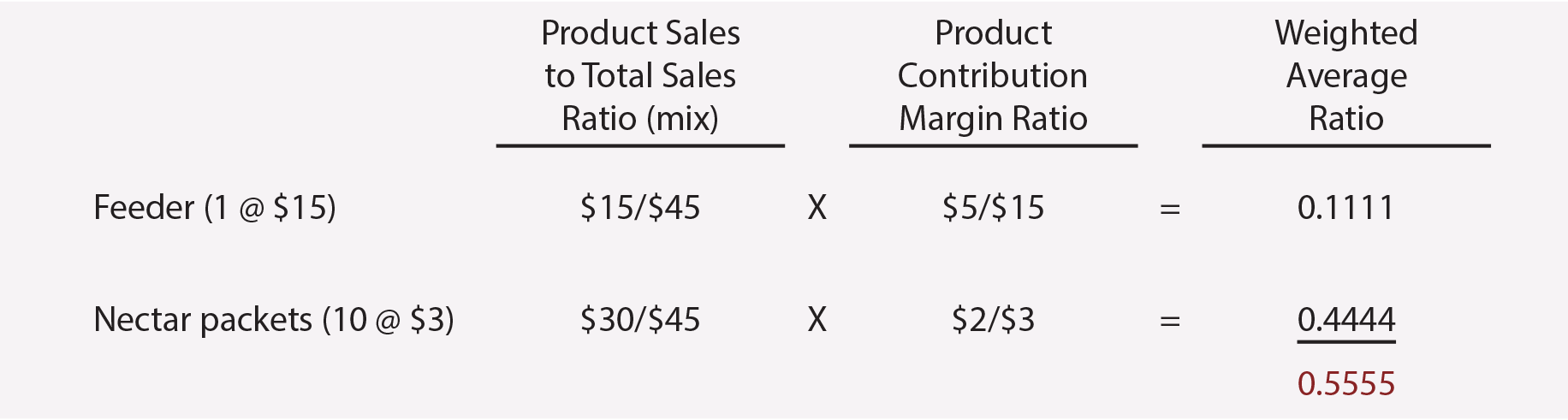
Note that one could also get the $180,000 result by dividing the fixed cost by the weighted-average contribution margin ($100,000/0.555 = $180,000). The weighted-average contribution margin of 0.555 is calculated as follows:
Businesses must be mindful of the product mix. Automobile manufacturers have a broad range of products, some at high margin and some at lower levels. If customers unexpectedly substitute economy cars for sport utility vehicles or basic models for luxury models, the resulting bottom line impacts can be significant.
Product mix can also be important for companies that sell a base product and a related disposable. For example, a printer manufacturer may sell “unprofitable” printers along with large quantities of high margin ink cartridges.
Multiple Products, Selling Costs, And Margin
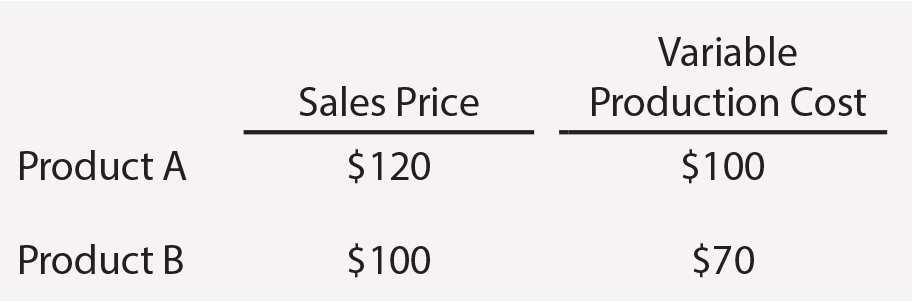 Selling expenses may be variable. For example, a salesperson may be paid a designated percentage of total sales. Such arrangements have the potential to be counterproductive in a multiple-product setting.
Selling expenses may be variable. For example, a salesperson may be paid a designated percentage of total sales. Such arrangements have the potential to be counterproductive in a multiple-product setting.
For example, assume that a company sells two products. Product A has a per unit sales price of $120, and Product B has a per unit sales price of $100.
A salesperson, earning a commission calculated as 5% of total sales, would prefer to sell product A. However, the company is better off when Product B is sold, because it has a higher contribution impact ($30 vs. $20). As a result, when a business manager considers its program of compensation for its sales staff, care should be given to align the interests of the sales force and the company. For the preceding example, it may make better sense to tie the commission to the contribution effects rather than the sales price.
| Did you learn? |
|---|
| Be able to apply CVP analysis to firms with multiple products. |
